You don’t have to be a health or nutrition expert to know that eating vegetables is important. From your earliest of days, you were probably told to “eat your vegetables” at dinnertime and may have even been incentivized to do so. As an adult, you are likely still aware of the importance of getting enough vegetables into your diet, yet you may have questions about which ones are best and why.
As it is with most foods, there is a lot of variety when it comes to vegetables, and different types have different health benefits. We’re here to help break down vegetables, including why they’re important, what the different types are, and which ones to focus on for your best health and why.
Why are Vegetables Important?
Vegetables are one of the healthiest food groups you can eat. They contain a wide variety of nutrients while being naturally low in calories and contain virtually no fat, sodium or sugar. The current 2015-2020 dietary guidelines for Americans recommends eating at least two and a half cups of vegetables each day. However, most people aren’t eating enough and are missing out on many important health benefits.

Some of these health benefits of vegetables include:
- Reduces risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes– there is an abundance of evidence that shows that diets rich in both fruits and vegetables can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke. Because many vegetables are also low on the glycemic index, they can also support normal blood sugar levels and can reduce the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
- May help lower blood pressure– many vegetables are a rich source of potassium, which is a key nutrient in balancing blood pressure. They are also an important component to the DASH diet, which was designed to help manage blood pressure and has been linked to significant reductions in blood pressure levels in those who follow it.
- Helps protect against cancer– vegetables are a rich source of antioxidants, which fight against free radicals in the cells that can cause cancer. They also contain plant compounds called phytochemicals, which are shown by research to be cancer-protective.
- Supports a healthy weight– thanks to being low in calories and high in fiber, eating vegetables is shown to help prevent obesity and support weight loss. Fiber adds bulk to the diet which contributes to a feeling of fullness, so it is nearly impossible to overeat on vegetables.
- Supports gut health– The fiber that vegetables contain also helps protect against digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome and constipation. Some vegetables are also a source of prebiotics, which work with probiotics to help support a proper balance between good versus bad bacteria in the gut, also known as the microbiome. You can read more about gut health and its impact on the whole body in this post.

Get Accountability + Support to Improve Your Nutrition. Join the CleanFoodCrush Challenge!
The Different Types of Vegetables, Explained
There are many different categories of vegetables, and some vegetables fall into more than one category. While all vegetables contain important nutrients and health benefits, there are some instances where certain types may need to be limited for people with specific health conditions.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the main groups of vegetables including reasons to eat them as well as potential cautions to watch out for:
 Starchy Vegetables
Starchy Vegetables
Starch is a type of complex carbohydrate that is found in many foods including breads, pasta and cereals. Some vegetables are also high in starch, including potatoes, corn, peas, yams, taro, pumpkin, butternut and acorn squash.
 Reasons to eat: starchy vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals including vitamin C and potassium. They are also a good source of resistant starch, which acts like fiber during digestion and feeds the beneficial bacteria in the digestive tract. Because they contain more calories than other vegetables, they can also be more filling.
Reasons to eat: starchy vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals including vitamin C and potassium. They are also a good source of resistant starch, which acts like fiber during digestion and feeds the beneficial bacteria in the digestive tract. Because they contain more calories than other vegetables, they can also be more filling.
 Potential cautions: In addition to being higher in calories, starchy vegetables are also higher in carbohydrates compared to their non-starchy counterparts, so they may need to be limited in people trying to control their blood sugar and/or manage their weight.
Potential cautions: In addition to being higher in calories, starchy vegetables are also higher in carbohydrates compared to their non-starchy counterparts, so they may need to be limited in people trying to control their blood sugar and/or manage their weight.
 Non-Starchy Vegetables
Non-Starchy Vegetables
These contain lower amounts of starch and include the remaining vegetables that are not classified as starchy. Examples include asparagus, mushrooms, onions, bell peppers, cucumber, celery, and zucchini.
 Reasons to eat: because non-starchy vegetables are lower in calories and carbohydrates, they can be eaten in virtually unlimited amounts without causing a blood sugar spike or contributing to excessive energy intake. They contain a wide variety of important nutrients and are associated with a variety of health benefits, as described above.
Reasons to eat: because non-starchy vegetables are lower in calories and carbohydrates, they can be eaten in virtually unlimited amounts without causing a blood sugar spike or contributing to excessive energy intake. They contain a wide variety of important nutrients and are associated with a variety of health benefits, as described above.
 Potential cautions: some non-starchy vegetables fall into other categories (listed below) that may warrant limiting their intake for people with specific health conditions.
Potential cautions: some non-starchy vegetables fall into other categories (listed below) that may warrant limiting their intake for people with specific health conditions.

 Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous Vegetables
This class of vegetables includes broccoli, cauliflower, brussels sprouts, cabbage, bok choy, turnips, collard greens, arugula, radishes, watercress, kale, and a few others.
 Reasons to eat: Cruciferous vegetables are specifically linked to a reduced risk of many types of cancers. Research also shows that cruciferous vegetables support the body’s natural ability to detoxify and well as fight inflammation, which further protects from disease and other health ailments.
Reasons to eat: Cruciferous vegetables are specifically linked to a reduced risk of many types of cancers. Research also shows that cruciferous vegetables support the body’s natural ability to detoxify and well as fight inflammation, which further protects from disease and other health ailments.
 Potential cautions: cruciferous vegetables are known for being especially gas producing for sensitive people, so those with abnormal bowel habits including irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease may need to limit their intake.
Potential cautions: cruciferous vegetables are known for being especially gas producing for sensitive people, so those with abnormal bowel habits including irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease may need to limit their intake.
 Nightshades
Nightshades
These are another class of vegetables that belong to a specific plant family, and include a combination of starchy and non-starchy vegetables. Tomatoes, peppers, white potatoes, and eggplant are all common nightshade vegetables.
 Reasons to eat: nightshades provide important vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants to support overall health.
Reasons to eat: nightshades provide important vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants to support overall health.
 Potential cautions: there are some reports that eating nightshades may be harmful for people with autoimmune conditions, digestive disorders, or food sensitivities. However, there is a lack of research supporting this. In general, nightshades should only be limited in people who experience symptom improvement after a trial of eliminating them.
Potential cautions: there are some reports that eating nightshades may be harmful for people with autoimmune conditions, digestive disorders, or food sensitivities. However, there is a lack of research supporting this. In general, nightshades should only be limited in people who experience symptom improvement after a trial of eliminating them.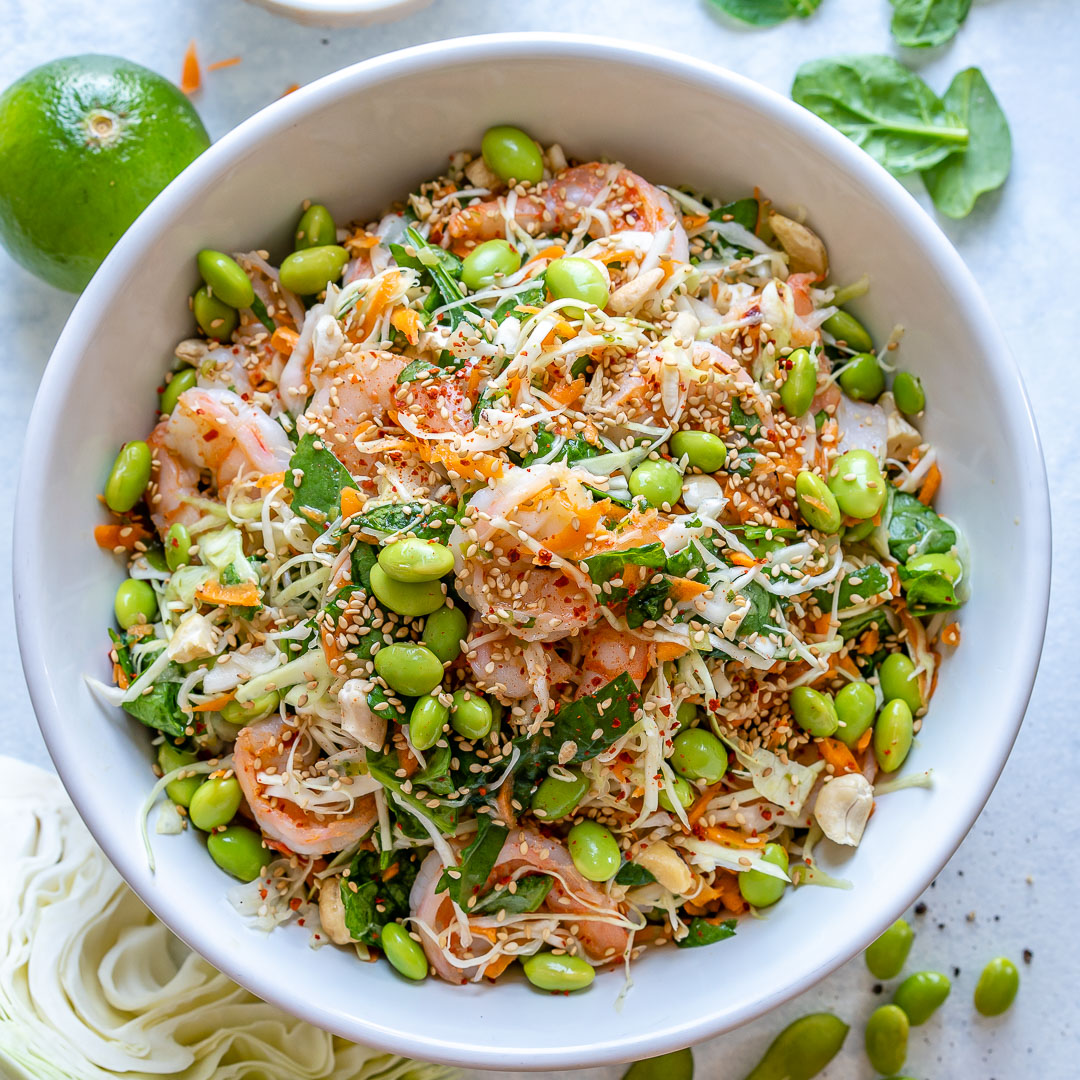 
Get Your Veggies On With This Thai Inspired Salad!
 Leafy Green Vegetables
Leafy Green Vegetables
These include things like lettuce, arugula, spinach, kale, cabbage, swiss chard, and mustard greens.
 Reasons to eat: leafy greens are a rich source of potassium, folate, vitamin K and others and have been specifically shown to be helpful for heart disease prevention as well as for slowing mental decline associated with aging.
Reasons to eat: leafy greens are a rich source of potassium, folate, vitamin K and others and have been specifically shown to be helpful for heart disease prevention as well as for slowing mental decline associated with aging.
 Potential cautions: there are no known risks with eating leafy green vegetables as a whole group. However, since some leafy greens like kale and cabbage also fall into the cruciferous vegetable category, people with sensitivities to those may need to limit their intake.
Potential cautions: there are no known risks with eating leafy green vegetables as a whole group. However, since some leafy greens like kale and cabbage also fall into the cruciferous vegetable category, people with sensitivities to those may need to limit their intake.
 Allium Vegetables
Allium Vegetables
This is another class of vegetables that include onions, shallots, and garlic.
 Reasons to eat: Garlic contains natural antimicrobial properties and may help boost the immune system. Research also supports its use for treating individuals with diabetes, hypertension, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
Reasons to eat: Garlic contains natural antimicrobial properties and may help boost the immune system. Research also supports its use for treating individuals with diabetes, hypertension, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
 Potential cautions: Allium vegetables are high in types of carbohydrates known as FODMAP’s, which may be detrimental to people with irritable bowel syndrome, leaky gut, and other digestive problems.
Potential cautions: Allium vegetables are high in types of carbohydrates known as FODMAP’s, which may be detrimental to people with irritable bowel syndrome, leaky gut, and other digestive problems.

In Summary
Vegetables are one of the healthiest food groups and should be eaten on a daily basis. No matter what type of diet you follow or what health conditions you may have, there are many vegetables that can be enjoyed. Understanding the different categories of vegetables can help you determine which ones may be most beneficial to focus on for your specific health goals. It is always best to work with a trusted healthcare practitioner when making modifications to your diet to help ensure you’re best meeting your unique needs.

from Clean Food Crush https://ift.tt/38eChHi



No comments:
Post a Comment