Chances are you’ve been seeing or hearing a lot about collagen lately. Whether or not you’ve tried it yet, you’ve probably seen it advertised in the media or stocked on grocery store shelves. Like most new health products, though, you might be wondering whether collagen is worth spending money on, and whether it is all that it’s hyped up to be.
Keep reading to learn more about what collagen is, what it does, and reasons why you may consider starting to add it to your diet.
What is Collagen?
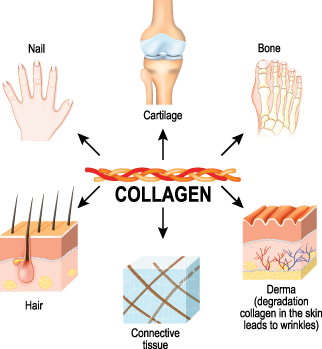
Collagen is one of the most abundant proteins in the body and is a major component of connective tissue, which includes tendons, cartilage, and ligaments. Collagen is also a building block of our skin and digestive tract lining.
Put simply, collagen can be thought of as a “glue” that helps provide support and holds things in our bodies together.
Collagen is considered an incomplete protein due to the fact that it is missing the amino acid tryptophan. However, this is not considered significant since it is very possible to get all of the essential amino acids by eating a variety of protein foods throughout the day and week.
What are the Benefits of Collagen?
There are many different types of collagen, and they each play important roles in the body. Because it is widely present in the body, it is associated with many health benefits*, such as:
- Skin health. Collagen is an essential component to skin, and is known to help improve skin elasticity and protect against premature wrinkles and other signs of aging.
- Wound Healing. Along with its role in skin health , it has also been shown to help accelerate wound healing, including pressure ulcers.
- Joint health. Since it is an essential component to connective tissues, collagen supports flexibility in the joints, tendons, ligaments and muscles. This can help protect against injury and is also beneficial for conditions such as arthritis.
- Gut health. Collagen is a component of the tiny hairlike structures called villi, which make up the intestinal wall. It has been used to treat digestive disorders such as leaky gut. It is believed to help seal the gut lining and reduce inflammation which can help improve negative digestive symptoms.
- Bones. Collagen helps provide structure to bones, and may support bone health by improving overall bone mineral density.
*Keep in mind that the research on the health benefits of collagen is limited and more studies are needed to confirm findings.
How Can You Include Collagen in Your Diet?
Below are some of the most common sources of collagen in the diet along with things that naturally help boost its production in the body:
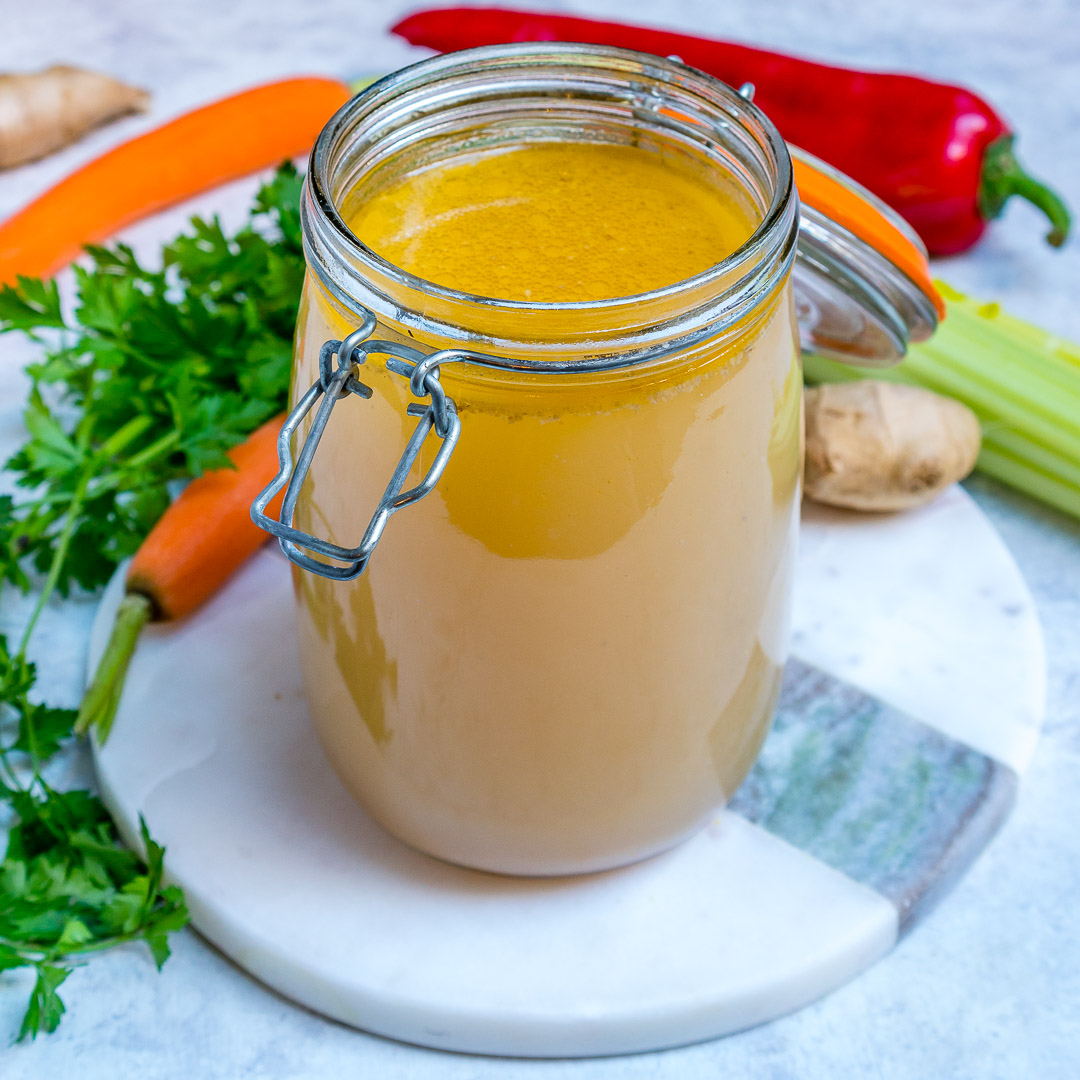
- Bone broth. Unlike traditional stock, which is typically simmered for only a few hours, bone broth is often simmered for multiple hours to help break down the bones and release as many nutrients and minerals as possible from them, including easily absorbable vitamins like zinc, calcium, and phosphorus and beneficial amino acids like glycine. Bone broth can be made at home or purchased in many grocery stores, and is a good source of protein as well. Bone broth protein powder has also more recently become an option to buy and use.
- Collagen supplements. These are made from animal skin, primarily cattle or fish. They are often purchased in the form of collagen peptides, which are smaller amino acid chains that make collagen more easily absorbed and utilized in the body, since the body can’t absorb collagen in whole form. Collagen peptides come in a powder form and can be flavored or unflavored and used in a variety of ways.
- Animal products. Since collagen is concentrated in connective tissues, any meat that contains muscle or other connective tissue will be a rich source. Slow cooked, bone-in meats are a great natural source of collagen.
Try Our Slow-Cooker Homemade Bone Broth To Boost Collagen Naturally
In addition, many nutrients help support collagen production, such as:
- Vitamin C, which is both a vitamin and a powerful antioxidant that stimulates collagen synthesis. Good food sources include strawberries, citrus fruits, tomatoes and bell peppers, among others.
- Other antioxidants, which help fight off damaging free radicals and protect against collagen destruction. Food examples include berries, green tea, pomegranate,
- Protein rich foods, which will help supply the amino acids that are required to produce collagen. Good food sources include fish, poultry, eggs, some dairy products, and lean beef or pork.
What Increases Collagen Needs in the Body?
Collagen is present in all human bodies, but there are some factors that cause it to be destroyed and therefore increases needs in the body. These include:
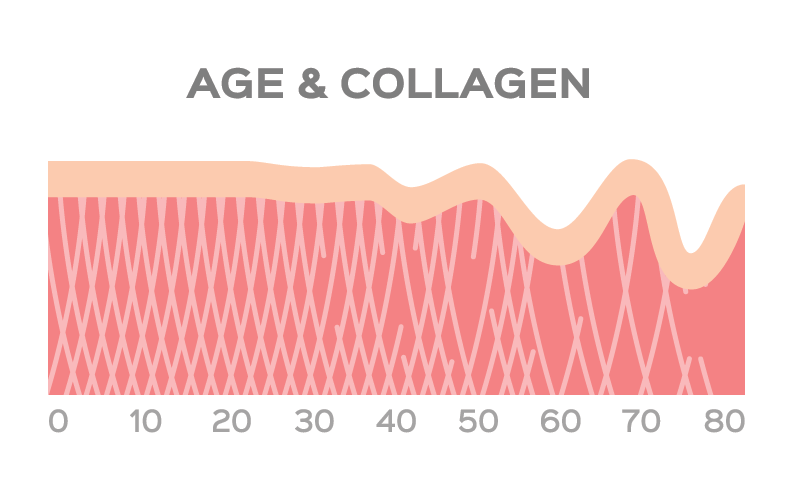
- Age. Collagen production decreases with age. This is partly why aged skin tends to have more wrinkles and be thinner and looser than younger skin. It also helps explain why older adults are more prone to joint pain, weakened muscles, and less flexibility.
- Poor diet. The body requires certain nutrients and amino acids from protein in order to produce collagen. Eating an imbalanced diet that is low in high quality protein and high in refined carbohydrates and sugar can impair collagen production.
- Smoking. Smoking impairs collagen synthesis, which may also be why smokers tend to have older looking skin sooner in life, as well as delayed wound healing
- UV rays from the sun. There are many benefits of sun exposure, but too much can reduce collagen production, also leading to older looking skin.
- Pregnancy. Collagen is a rich source of the amino acid glycine, which is needed in higher amounts during pregnancy for baby’s growth and development.
In Summary
Collagen isn’t necessarily the miracle food or supplement that the media can make it seem to be, but it does pose some important potential health benefits and is worth trying or using regularly for those who are interested. There are a variety of ways to make sure you’re consuming enough collagen and supporting its production in your body, so it may not be as difficult to obtain as some people may think. Working with a trusted healthcare practitioner can help determine whether or not placing more emphasis on collagen makes sense for you and your unique health and lifestyle.

from Clean Food Crush https://ift.tt/2Cjl4OW




No comments:
Post a Comment